Bird flu, also known as avian influenza, is a viral infection that primarily affects birds, especially wild waterfowl and domesticated poultry. While bird flu mainly impacts animals, certain strains of the virus have the potential to infect humans, leading to serious health complications. The most well-known and dangerous strains of avian influenza for humans are H5N1 and H7N9.
Understanding the symptoms of bird flu in humans is crucial, especially for those who work closely with poultry or live in regions where outbreaks have been reported. Although human-to-human transmission of bird flu is rare, the disease can still lead to severe illness and death. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore bird flu symptoms in humans, how the virus spreads, the potential risks, and what you can do to protect yourself from infection.
Symptoms of Bird Flu in Humans – What is Bird Flu?
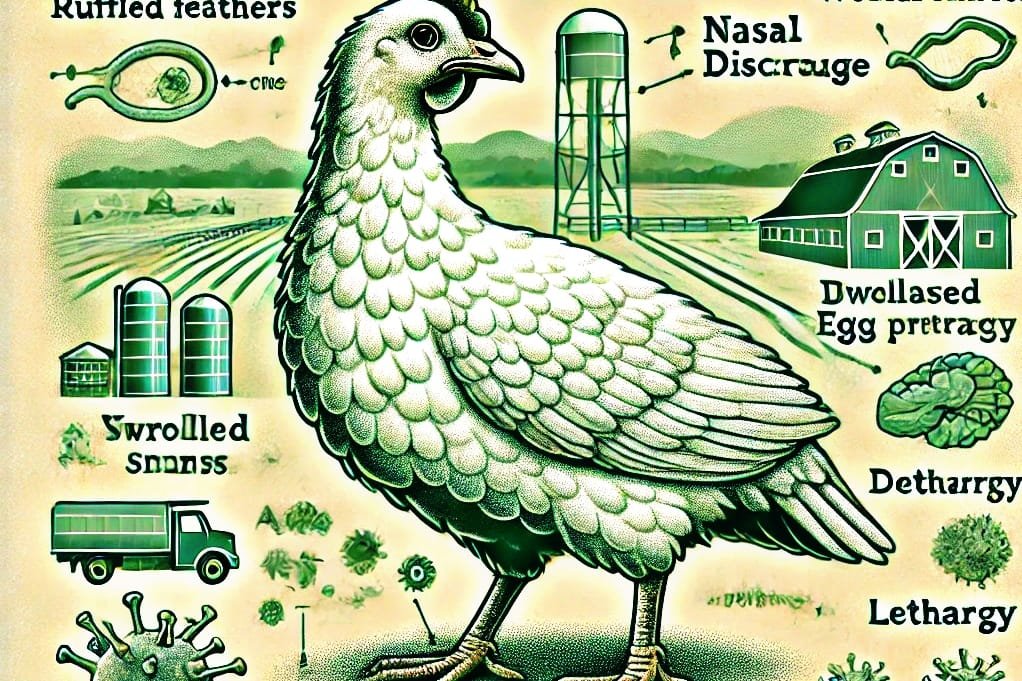

Bird flu is caused by the avian influenza virus, which infects birds, particularly wild birds, poultry, and sometimes other animals. While most avian influenza viruses do not infect humans, certain strains have the potential to cross the species barrier. These strains are often referred to as zoonotic viruses, meaning they can be transmitted from animals to humans.
The most concerning of these strains are H5N1, H7N9, and H5N8. These viruses have caused significant public health concern due to their potential to cause severe illness in humans. However, human-to-human transmission remains relatively uncommon, and most cases occur after close contact with infected birds or contaminated environments.
How Does Bird Flu Spread to Humans?
The primary way Symptoms of Bird Flu in Humans is through direct or indirect contact with infected birds, their droppings, feathers, or contaminated environments. This is particularly a risk for people working in poultry farms or live bird markets. Additionally, handling or consuming undercooked poultry products can also lead to infection.
Human-to-human transmission of bird flu is extremely rare but can happen in certain circumstances. Some strains, such as H5N1 and H7N9, have shown limited ability to spread from person to person, though the transmission is usually not sustained. Health experts are most concerned about the possibility that these viruses could mutate and become more easily transmissible between humans, leading to a pandemic.
The virus is typically transmitted when a person comes into contact with infected birds, particularly in environments where the birds have close contact with one another. The virus can be shed through bird saliva, nasal secretions, and feces, which makes it easy for the virus to spread within a poultry farm or market. Humans can contract the virus by handling infected birds or being exposed to contaminated areas.
Most Common Symptoms of Bird Flu in Humans
When Symptoms of Bird Flu in Humans, the symptoms often resemble those of the seasonal flu but can escalate quickly, especially with certain strains like H5N1 and H7N9. It’s essential to recognize these symptoms early to seek proper medical care, as early antiviral treatment can reduce the severity of the illness.
1. Fever and Chills
One of the most common symptoms of bird flu in humans is fever, which is typically high-grade, often above 101°F (38.3°C). Chills often accompany the fever and can cause discomfort. These symptoms are common in many viral infections, including seasonal flu, but they can be much more intense with bird flu.
2. Cough
A persistent dry cough is another hallmark symptom of avian influenza in humans. This cough can become severe and is often accompanied by a sore throat. As the infection progresses, the cough may worsen, and phlegm or mucus may be produced. In severe cases, the virus can lead to pneumonia, making the cough even more debilitating.
3. Sore Throat and Runny Nose
In addition to a dry cough, individuals infected with bird flu may experience a sore throat and nasal congestion or a runny nose. These symptoms are often present early in the illness and can make it challenging to distinguish bird flu from other upper respiratory infections, such as the common cold or seasonal flu.
4. Fatigue and Body Aches
Fatigue is another common symptom of bird flu in humans. People infected with the virus often report feeling extremely tired and weak, which may last for several days or even weeks. Along with fatigue, muscle aches and joint pain are also common. These body aches can be severe and are often accompanied by chills and fever.
5. Headache
A headache is a frequent symptom of many viral infections, including bird flu. The headache can be mild to severe and is usually accompanied by other flu-like symptoms, such as fever and fatigue.
6. Shortness of Breath and Chest Pain
As the infection progresses, it can cause significant respiratory distress. Shortness of breath and chest pain are signs that the virus may have led to pneumonia or severe lung involvement. Pneumonia is a common complication of severe bird flu and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Individuals with pneumonia may experience difficulty breathing, wheezing, and a rapid heart rate.
7. Nausea, Vomiting, and Diarrhea
Some strains of the avian influenza virus, especially H5N1, have been associated with gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. While these symptoms are not as common as respiratory symptoms, they can still occur and may be indicative of a severe infection.
8. Eye Infections (Conjunctivitis)
Some strains of bird flu, such as H5N1, can cause eye infections in humans, which may manifest as redness, swelling, and irritation in the eyes. This condition, called conjunctivitis, is more common in regions where the virus is circulating among birds.
9. Cyanosis
In severe cases of bird flu, a condition called cyanosis may occur, which is a bluish tint to the skin, lips, or nails. This occurs due to a lack of oxygen in the blood, which can be caused by severe respiratory distress or pneumonia. Cyanosis is a serious symptom and requires immediate medical attention.
10. Confusion and Seizures
In rare and severe cases of avian influenza, the virus can affect the brain and lead to confusion, delirium, or even seizures. This is more likely to occur in individuals with severe pneumonia or who are in critical condition.
Symptoms of Bird Flu in Humans – Severe Symptoms of Bird Flu
While most individuals infected with avian influenza will experience mild to moderate symptoms, in severe cases, bird flu can cause life-threatening complications. If not treated promptly, the virus can lead to:
- Respiratory failure: As the virus spreads to the lungs, it can cause severe pneumonia, which may result in respiratory failure and the need for mechanical ventilation.
- Organ failure: Severe infection can lead to organ failure, including kidney or liver failure, which significantly increases the risk of death.
- Sepsis: In severe cases, the infection can cause sepsis, a systemic inflammatory response that can lead to multi-organ failure and death.
Individuals at higher risk for severe disease include the elderly, children, pregnant women, and those with weakened immune systems or pre-existing health conditions.
Symptoms of Bird Flu in Humans – Risk Factors for Bird Flu Infection
While the risk of contracting Symptoms of Bird Flu in Humans is low, certain factors increase the likelihood of infection. Understanding these risk factors can help people take necessary precautions:
- Close Contact with Infected Birds: People who work with poultry, especially those who handle live birds or their droppings, are at the highest risk of infection.
- Handling or Consuming Undercooked Poultry: Bird flu can be transmitted through the consumption of undercooked poultry or eggs from infected birds.
- Geographic Location: People living in or traveling to areas with known bird flu outbreaks are at higher risk of exposure to the virus.
- Weak Immune Systems: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as the elderly, young children, and those with chronic health conditions, are more susceptible to severe disease.
Symptoms of Bird Flu in Humans – Treatment and Prevention
There is no specific vaccine for Symptoms of Bird Flu in Humans, although vaccines are available for certain strains of avian influenza in poultry. Early detection and antiviral treatment can significantly reduce the severity of the disease and improve outcomes.
1. Antiviral Medications
Antiviral drugs, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza), can be used to treat bird flu if administered early. These medications are most effective when given within 48 hours of the onset of symptoms and can help reduce the severity and duration of the illness.
2. Supportive Care
For individuals with severe symptoms, especially respiratory failure or pneumonia, supportive care in a hospital setting may be necessary. This can include oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, and fluids to manage dehydration.
3. Preventive Measures
- Avoiding Contact with Infected Birds: The most important preventive measure is to avoid contact with birds that are suspected to have the virus. This includes avoiding live bird markets and areas with known outbreaks.
- Hand Hygiene: Regularly washing your hands with soap and water can help prevent the spread of the virus.
- Cooking Poultry Thoroughly: Ensure all poultry is cooked to an internal temperature of at least 165°F (74°C) to kill any potential virus.
Conclusion – Symptoms of Bird Flu in Humans
While the symptoms of bird flu in humans can range from mild to severe, understanding the early warning signs is crucial for early intervention and treatment. Prompt medical care, especially antiviral treatment, can significantly improve the chances of recovery from avian influenza.
Although the risk of human infection remains relatively low, individuals who work with poultry, live in affected regions, or are exposed to infected birds should take necessary precautions. By staying informed, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding high-risk activities, you can protect yourself from the potentially dangerous effects of bird flu.
Remember, if you experience any of the symptoms of bird flu in humans, especially after exposure to sick or dead birds, seek medical attention immediately. Early detection and treatment are key to reducing the risk of serious complications and ensuring a full recovery.